About Museum of Spiš Territory
Museum of Spiš teritory in Spišská Nová Ves resides in historical building former medieval Town Hall since 1954. The most interesting architectonic town monument is situated on the north side of the longest square of lenticular shape in Europe - in opposite of parish church with the highest Tower in Slovakia. Today's look obtained this building after re-building in 1765. Facade is decorated by rococo stucco decoration of six cartouches which presents assumed natures of mayors.In 1777 the Province of XVI Spiš towns bought town hall for its purposes. From there becomes the name Provincial House. After fall of the Province, the House was given for hire and after it the House was bought from Spiš Župa. In year 1894 it was bought by Sporiteľňa (Savings Bank) of XVI Spiš towns. According with decision of Town Council (Rada ONV v Spišskej Novej Vsi) the Museum arose on May 7th, 1951 and museum expositions are there from 1955.
A name of the Museum was changed during its existence: 1951 - Regional Homeland Museum, 1955 - Homeland Natural Museum, 1971 - Homeland Museum of Spiš with Gallery, 1984 - Homeland Natural Museum, 1996 - Spiš Museum in Spišská Nová Ves, 1997 - Museum of the Spiš Region, Also expositions were changed during existence of the Museum. Contemporary Exposition of Nature and History of the Region Spiš was installed in 1992. It provides to visitor characteristics of geographic, geological, paleontological, botanic and zoological orographic units: Slovenský raj National Park, Spišskogemerské rudohorie Ore Mountains, Hornádska kotlina Valley and Levočské vrchy Mountains, whereby particularities, curiosities and unique of the nature presented territory are in every part. History of the Region is presented through exhibits of collection funds from archaeology, mining activities and crafts.
Branches of the Museum
| Markušovce Manor House | Historic furniture exposition |
| Dardanely Summer-House | Exposition of key musical instruments |
| Smižany Ethnic Museum | Exposition of folk culture on the territory of Middle and Lower Spiš |
| House of birth of Capt. Ján Nálepka |
Exposition of the Museum of the Spiš Region Ground Plan of the Exposition on the Storey
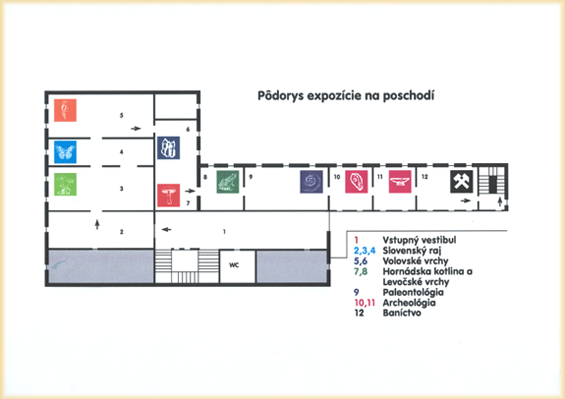
| 1 | ENTRANCE HALL-photo prints and introductory information about Museum of the Spiš Region |
| 2 3 4 | NATIONAL PARK SLOVENSKÝ RAJOne of the worthiest natural territories of Slovakia. Typical karst territory of West Carpathian Mountains characteristic by geomorphologic variety, diversiform geological building, specific heterogeneity of flora and fauna. On the territory of Slovenský raj are registered about 378 caves. Open for public is only one of them Ice cave Dobšinská ľadová jaskyňa, which was in 2000 enrolled in to World Heritage List of the cultural and natural heritage UNESCO: 930 upper species of plants, 4 000 species of invertebrates and 200 species of vertebrates. |
| 5 6 | VOLOVSKÉ VRCHY MOUNTAINSNatural values, occurrence of minerals and ore exploitation had important economic influence for inhabitants of region. It is well-preserved natural territory with occurrence of many species of preserved animals and plants. The exposition presents lower and upper plants, zoological specimens of mountain and forest species of animals, basic types of rocks and samples of minerals, which represent Cu, Fe, Hg, Au, Ag ores. |
| 7 8 | HORNÁDSKA KOTLINA VALLEY AND LEVOČSKÉ VRCHY MOUNTAINSThe territory is at most impacted by human activity. Travertine heaps of surrounding of Spišské Podhradie create the worthiest natural part of the territory. There were declared for National natural reservations: Dreveník, Sivá Brada, National natural sights: Spišský hradný vrch (Spiš Castle Hill) and natural sights: Ostrá hora and Sobotisko. |
| 9 | PALEONTOLOGYThe newest part of exposition (1993) presents unique paleontological finds from this region. Fossils of mastodon Mammut borsoni (Hays, 1834), mould of turtle Emys orbicularis, fossils of Permian flora genus Cordaitopsida and cave bear Ursus spelaeus are the most important from 165 pieces on view exhibits. |
| 10 11 | ARCHAEOLOGYThere are 598 pieces of archaeological collections (tools, applied art articles, outfit and jewellery) document development of human society in this region from the time of Stone Age up to the Middle Ages. |
| 12 | MINING ACTIVITIESMining activity influenced during centuries economic and cultural life in the region. There are demonstrations of mining tools, measuring instruments, lighting devices and others, which approach this part of history. |


